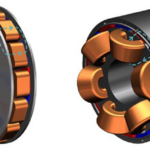
Radial flux AC motors offer some performance and packaging benefits but also bring some thermal and manufacturability issues. For many electrical and even mechanical engineers, motor selection is somewhat of a mysterious process. You can understand their basic principles and operation. Still, the real-world design considerations of their flux paths, poles, materials, and tradeoffs seems […]
Featured
Danisense to exhibit at APEC 2024
Danisense will be exhibiting at APEC 2024 at Long Beach Convention Center, Long Beach, California, USA, from 25th to 29th Feb 2024 at booth 834 of its US distribution partner GMW Associates. On display will be several highly precise and reliable current sense transducers from Danisense. Featuring a very large aperture of 41.2mm, the DN1000ID […]
Murata launches three power systems
Murata announces a trio of products, including a new charge pump IC and two step-down DC-DC converters designed to solve power challenges for consumer devices and low-output voltage applications Murata, at the 2024 Applied Power Electronics Conference (APEC), announced the launch of three new power product solutions designed to help solve the challenges, constraints, and […]
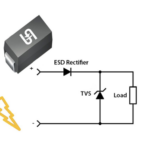
400 V/600 V ESD withstand-capable rectifiers offering both polarity protection and ESD protection
New TSD Series automotive-qualified 400 V / 600 V rectifiers target a wide range of lighting, industrial, communications, security, and many other applications requiring robust ESD protection. Taiwan Semiconductor announces its new line of automotive-qualified rectifiers featuring ESD withstand capability. The TSD Series rectifiers simultaneously provide repetitive peak reverse voltage (VRRM) of up to 600 […]
Cambridge GaN devices moves to support industrial applications
Cambridge GaN Devices (CGD) is addressing higher power industrial applications with its ICeGaN™ technology, which has already proved itself rugged, reliable, and easy to use in high-volume consumer devices. At the APEC 2024, IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, the company is introducing new reference designs and showing demos that address the broad and […]
Switcher IC family boasts multiple, independently regulated outputs
GaN-based ICs combine AC-DC and DC-DC stages into a single power converter, cutting power system losses by up to 50 percent. Power Integrations announces the InnoMux™-2 family of single-stage, independently regulated multi-output offline power-supply ICs. InnoMux-2 ICs consolidate AC-DC and downstream DC-DC conversion stages into a single chip, providing up to three independently regulated outputs […]
New USB-C reference designs & finished modules with more than 95% average efficiency
Pulsiv Limited is set to release a series of reference designs and assembled modules for USB-C applications that will deliver an average efficiency of more than 95%. This groundbreaking achievement, which minimizes energy waste under all operating conditions, has been developed in collaboration with GaN leader, Innoscience, and magnetics expert Frenetic. Designs will be released […]
AmberSemi showcases power products with ST embedded solutions
At APEC 2024, the companies will showcase reference designs for brushless motors jointly developed using AmberSemi’s AC Direct DC Enabler Power Conversion Technology and ST’s STM32 MCU devices. Amber Semiconductor, Inc. announced a reference design for brushless motor applications using AmberSemi’s breakthrough AC-to-DC conversion semiconductor system to power ST’s STM32 microcontrollers. This reference design will […]
ROHM’s EcoGaN adopted in the 45W output USB-C charger C4 duo from Innergie
ROHM Semiconductor announces the adoption of its 650V GaN device (EcoGaN™) in the C4 Duo, a 45W output USB-C charger from Innergie, a brand of Delta. ROHM’s EcoGaN device contributes to greater application performance, reliability, and miniaturization by providing higher efficiency in power supply systems. Efforts to save energy are accelerating toward achieving a decarbonized […]
Delivering power supply reliability in mission-critical systems
There are several factors to consider when selecting a power supply that delivers the high voltages often needed by large and complex high-performance systems. For almost all electronic products and systems, high reliability should be expected. Still, in some markets, reliability cannot be compromised or a trade-off for other performance factors. In particular, mission-critical industrial […]