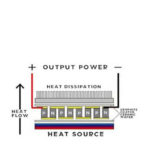
Thermoelectric cooling, using a Peltier module, gives designers flexibility to cool objects to a precisely controlled temperature, even below the ambient temperature of the application if required. It is a great choice if forced-air cooling is not possible, and a thermoelectric device is typically smaller, lighter and more energy-efficient than cooling using a compressor and dissipative heater. In addition, a Peltier module can work in any orientation.
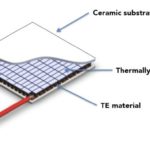
The modules take advantage of the Peltier effect, which produces a temperature differential as a current passes through a semiconductor structure. Depending on the design of the module, the quantity of thermal energy supplied and the current and voltage applied, a temperature differential exceeding 100°C can be achieved.
This CUI Insights blog, “How to Design a Peltier Module System” gives an overview of thermoelectric cooling and selection processes for choosing a suitable Peltier module for a given application. It also explains how the design of the thermoelectric system must take into account self-heating of the Peltier module, using feedback from a sensor for precise temperature control, and the role of other components such as the power supply in a complete Peltier module design.



Leave a Reply