By Brent McDonald, Texas Instruments Modern electronic systems need small, lightweight, high-efficiency power supplies. These supplies require cost-effective methods to take power from the AC power distribution grid and convert it to a form that can run the necessary electronics. High switching frequencies are among the most significant enablers for small size. To that end, […]
FAQ
How to quantify pulse current capability of SiC FETs
Silicon Carbide FETs go beyond silicon to extend reach to high pulse currents in power conversion applications. Wide bandgap (WBG) semiconductor devices, such as Silicon Carbide (SiC) field-effect transistors (FETs), are renowned for their minimal static and dynamic losses. Beyond these attributes, this technology can endure high pulse currents, proving particularly advantageous in applications like […]
Zonal automotive power distribution can dramatically improve efficiency, weight, and cost: part 3
If something can’t go on, it won’t; supplying the automobile’s voracious electrical demands from a 12-V battery is an example of this reality. If you haven’t already, check out Part 1 and Part 2 of this discussion. Under the zonal architecture, many legacy loads will still be supported by a 12-V battery or its functional […]
Zonal automotive power distribution can dramatically improve efficiency, weight, and cost: part 2
If something can’t go on, it won’t; supplying the automobile’s voracious electrical demands from a 12-V battery is an example of this reality. Topology changes affect the battery source Due to the 12-V issues, many newer ICE vehicles and nearly all EV/HEVs also have a 48-V battery. This battery serves loads that are more efficiently […]
Zonal automotive power distribution can dramatically improve efficiency, weight, and cost: part 1
If something can’t go on, it won’t; supplying the automobile’s voracious electrical demands from a 12-V battery is an example of this reality. Today’s cars — whether based on the traditional internal combustion engine (ICE), some form of hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), or even a pure electric vehicle (EV) — are loaded with electronics, sensors, […]
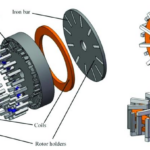
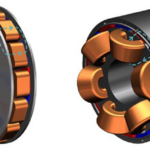
FAQ on axial flux motors: part 3
Radial flux AC motors offer some performance and packaging benefits but also bring some thermal and manufacturability issues. Part 1 of this series examined the axial-flux motor (AFM) in detail and compared it to the very widely used radial-flux motor (RFM). Part 2 of this FAQ continued the exploration of AFMs and RFMs. This final part […]
FAQ on axial flux motors: part 2
Radial flux AC motors offer some performance and packaging benefits but also bring some thermal and manufacturability issues. This part of the FAQ continues the exploration of AFMs and RFMs. The first part examined the axial-flux motor (AFM) in more detail and compared it to the very widely used radial-flux motor (RFM). The final part […]
FAQ on axial flux motors: part 1
Radial flux AC motors offer some performance and packaging benefits but also bring some thermal and manufacturability issues. For many electrical and even mechanical engineers, motor selection is somewhat of a mysterious process. You can understand their basic principles and operation. Still, the real-world design considerations of their flux paths, poles, materials, and tradeoffs seems […]
Delivering power supply reliability in mission-critical systems
There are several factors to consider when selecting a power supply that delivers the high voltages often needed by large and complex high-performance systems. For almost all electronic products and systems, high reliability should be expected. Still, in some markets, reliability cannot be compromised or a trade-off for other performance factors. In particular, mission-critical industrial […]
FAQ on servo motors: part 2
The servo motor is an older precise-positioning motor arrangement now facing some competition from the stepper motor. Part 1 of this article introduced the concept of servo motors along with servo amplifiers and servo controllers. This part continues that exploration. Q: What’s the history of servo motors? A: There were purely mechanical, closed-loop servo systems […]