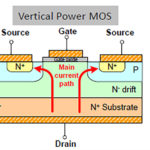
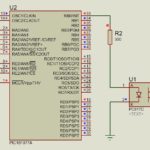
Power devices based on gallium nitride (GaN) are rapidly becoming a viable, higher-performance alternative to silicon MOSFETs due to their higher efficiency and other favorable attributes. In recent years, discrete power-switching and power-handling devices based on gallium nitride (GaN) material have become practical and available, and these devices are now found in many power supplies […]
basics
Working with higher voltages, Part 2: Voltage multipliers
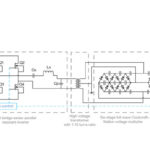
In part 1 of the FAQ, we looked at techniques for a modest amount of boosting of lower voltages, as well as for increasing a voltage to a much higher value. The techniques discussed thus far boost and thus multiply the voltage, but what are called voltage “multipliers” usually give push voltages to much-higher values. […]
Working with higher voltages, Part 1: Voltage boosters
Whether for efficiency or due to the device physics, many applications require voltages ranging in the tens, hundreds, or even thousands of volts; the circuits which produce these voltages start with basic charge pumps and extend to voltage multipliers with simple schematics but many subtleties. Lower-voltage circuitry is the trend, with ICs and designs operating […]
Thermal Electric Generators, Part 2: Applications
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the principles and components of a basic TEG system. Part 2 looks at some applications ranging from very small to large, and from scavenged auxiliary to primary power. Q: It seems like TEGs are costly and complicated, despite the simple principle of operation. Is this the case? A: […]
Thermal Electric Generators, Part 1: Principles and implementation
TEGs – thermal electric generators – are used for energy harvesting and enhanced efficiency, as well as stand-alone primary power sources for both mundane and highly advanced situations. Every application needs a source of energy which can be “drawn down” to provide power for the system. Obviously, the easier and cheaper it is to get […]
Why use optocouplers in electronics?
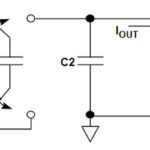
Optocouplers not only protect sensitive circuits but enable an engineer to design a variety of hardware applications. Optocouplers can avoid a great deal of cost in replacing components by protecting them. However, optocouplers are more sophisticated than fuses. Optocouplers also make it convenient to control the connection between two circuits by connecting and disconnecting them […]
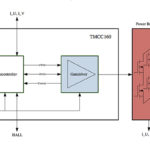
Motor field-oriented control, Part 2: Implementation
Part 1 of this FAQ set the stage for a rudimentary understanding of FOC (field-oriented control) but did not delve into the math-heavy details. Part 2 now looks at some implementations, again without the underlying math. Q: If a designer wants to implement FOC, does he or she have to pull together all the hardware […]
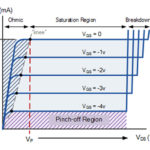
What’s the difference between a MOSFET and a JFET?
It’s a pretty common question for beginners and can be a fun walk down memory lane for experienced practitioners. Let’s take a dive into two fundamental devices of integrated circuits and learn when to use one over the other. How they are alike Let’s start with what they have in common: they are both types […]
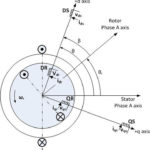
Motor field-oriented control, Part 1: Principles
Field-oriented control, also known as vector control, is a calculation-intensive algorithm for motor control which is now practical due to advances in ICs; it offers improved efficiency along with superior control of torque and other performance parameters. Motor control—and doing so accurately and efficiently—is a topic of great interest. Field-oriented control (FOC), sometimes called vector […]
Heat sinks, Part 2: Available components
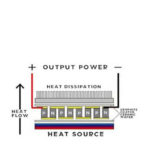
Part 1 of this FAQ looked at the basic issues associated with cooling and heat sinks. Part 2 focuses on the various heat sinks available. Q: Are heat sinks limited to a single component such as an IC? A: No, there are heat sinks which fit entire unit or chassis cool such as those which […]